Difference between revisions of "Old Testament"
m (Protected "Old Testament" [edit=autoconfirmed:move=autoconfirmed]) |
(removed video - has been taken down. removed categories Videos & Pages with YouTube content) (Tag: 2017 source edit) |
||
| (22 intermediate revisions by 12 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{quote | text={{ | + | {{quote | text={{Bible verse|Genesis|1|1|lang=WEB}} [[Genesis 1:1]]}} |
| − | |||
{{Infobox_Contents | | {{Infobox_Contents | | ||
topic_name = Old Testament | topic_name = Old Testament | ||
[[Image:Torah.jpg|thumb|center|The [[Torah]], part of the Old Testament.]] | | [[Image:Torah.jpg|thumb|center|The [[Torah]], part of the Old Testament.]] | | ||
| − | subtopics = [[Books of the Law]], [[Historical Books of the Old Testament]], [[Poetical Books of the Old Testament]], [[Prophetic Books of the Old Testament]] | + | subtopics = Divisions - [[Books of the Law]], [[Historical Books of the Old Testament|Historical Books]], [[Poetical Books of the Old Testament|Poetical Books]], [[Prophetic Books of the Old Testament|Prophetic Books]] |
| − | * [[ | + | * Languages - [[Biblical Hebrew]], [[Aramaic]] |
| − | + | * [[Ancient Israel and Judah]], [[Timeline of Biblical History]] | | |
| − | + | opinion_pieces = {{short_opinions}} | |
| − | * [[Ancient Israel and Judah]], [[Timeline of Biblical History]] | + | * [[An Introduction to the Old Testament (G.G.)]] | |
| − | |||
| − | opinion_pieces = {{short_opinions}} | | ||
}} | }} | ||
| + | {{ot}} | ||
| − | + | The Old Testament is the first major part of the [[Bible]], giving an account of God's interaction with the Jewish people through their history. To [[Christians]], the Old Testament is, throughout its pages, building up to the coming of [[Jesus]]. | |
| − | The Old Testament is the first major part of the [[Bible]], giving an account of | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | It consists of 39 books, that are often divided into the categories of law, history, poetry (or wisdom books) and prophecy. Within these categories, it gives an account of creation, and then follows the story of God's interaction with the Jewish people, through their slavery in Egypt, conquest of the promised land, strengthening kingdom, and finally its division and the people's exile. An brief approximate timeline of the [[Old Testament]] is shown below: | |
{{Brief_ot_timeline}} | {{Brief_ot_timeline}} | ||
| Line 30: | Line 25: | ||
The [[Old Testament]] is divided into 40 books in English. These books are not all written in the same style, but are different types of genres. Loosely, the genres are sometimes categorized as | The [[Old Testament]] is divided into 40 books in English. These books are not all written in the same style, but are different types of genres. Loosely, the genres are sometimes categorized as | ||
* Law | * Law | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
* History | * History | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
* Poetry and Wisdom | * Poetry and Wisdom | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
* Major Prophets | * Major Prophets | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
* Minor Prophets | * Minor Prophets | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
====Torah - [[Books of the Law]]==== | ====Torah - [[Books of the Law]]==== | ||
| Line 116: | Line 72: | ||
===Old Testament Geography=== | ===Old Testament Geography=== | ||
| − | [[Image:Satellite image of Israel in January 2003.jpg|thumb|A satellite image of Israel]] | + | [[Image:Satellite image of Israel in January 2003.jpg|thumb|A satellite image of Israel.]] |
An understanding of the geography of the region brings he stories of the Old Testament to life. There are 4 geographical north-south regions of Israel, in order of west to east: | An understanding of the geography of the region brings he stories of the Old Testament to life. There are 4 geographical north-south regions of Israel, in order of west to east: | ||
| Line 135: | Line 91: | ||
Apart from the [[Old Testament]], there is other literature from that time and region. Some of this literature includes creation stories and myths (such as the [[Enuma Elish]]), records from royal courts, conventants and laws, and poetry and wisdom literature from other ancient civilizations. These can be useful to help give more context (both in terms of type of literature and also in dating) to the Old Testament. | Apart from the [[Old Testament]], there is other literature from that time and region. Some of this literature includes creation stories and myths (such as the [[Enuma Elish]]), records from royal courts, conventants and laws, and poetry and wisdom literature from other ancient civilizations. These can be useful to help give more context (both in terms of type of literature and also in dating) to the Old Testament. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Quotes== | ||
==Links== | ==Links== | ||
* [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Old_Testament Wikipedia - Old Testament] | * [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Old_Testament Wikipedia - Old Testament] | ||
| − | {{returnto}} [[Bible]] | + | {{returnto}} [[Christianity]] -> [[Bible]] |
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Bible]] | ||
[[Category:Books of the Old Testament]] | [[Category:Books of the Old Testament]] | ||
Latest revision as of 01:58, 27 May 2021
|
In the beginning God created the heavens and the earth. Genesis 1:1
|
Old Testament
 The Torah, part of the Old Testament. | |
| RELATED TOPICS |
|
| SERMONS, ESSAYS AND OPINIONS | |
| CONTENTS | |
| Bible |
|---|
|
|
The Old Testament is the first major part of the Bible, giving an account of God's interaction with the Jewish people through their history. To Christians, the Old Testament is, throughout its pages, building up to the coming of Jesus.
It consists of 39 books, that are often divided into the categories of law, history, poetry (or wisdom books) and prophecy. Within these categories, it gives an account of creation, and then follows the story of God's interaction with the Jewish people, through their slavery in Egypt, conquest of the promised land, strengthening kingdom, and finally its division and the people's exile. An brief approximate timeline of the Old Testament is shown below:
| Estimated dates | Events |
|---|---|
| 1900-1700 BC | Patriarchs |
| 1700-1300 BC | Slavery in Egypt |
| 1300-1200 BC | Exodus and conquest |
| 1200-922 BC | United kingdom of Israel |
| 922-722 BC | Divided kingdom; northern kingdom exiled in 722 BC |
| 922-586 BC | Divided kingdom; southern kingdom exiled in 587 BC |
| 550 BC onwards | Return to Israel of Jews |
Although all of these books were written before the birth of Jesus Christ, they still show a picture of the same God that the New Testament does - the Old Testament also reveals a loving God of forgiveness and grace. To Christians, the Old Testament is, throughout its pages, building up to the coming of Jesus.
To Jewish people, the Old Testament is known as the "Tannakh", which is an acronym for the Torah (Genesis to Deuteronomy), Nebiim (Books of the prophets) and Kethubim (or Writings).
Books of the Old Testament
The Old Testament is divided into 40 books in English. These books are not all written in the same style, but are different types of genres. Loosely, the genres are sometimes categorized as
- Law
- History
- Poetry and Wisdom
- Major Prophets
- Minor Prophets
Torah - Books of the Law
The Torah consists of the first five books of the Bible. The first book, Genesis, tells about the creation of the universe and God choosing a person (Abraham) to be the father of his people. The next four books (Exodus to Deuteronomy) describe God saving his people from slavery in Egypt and giving them the law by which they were to live, including the Ten Commandments.
Historical Books of the Old Testament and Poetical Books of the Old Testament
Writings range from the historical such as Joshua, the Samuels, Chronicles, or Kings to poetry such as Song of Solomon, or Psalms and wisdom such as Job, Ecclesiastes, and Proverbs. They describe the nature of God such as Psalm 23, the wisdom of God and man's reaction such as in Job, or the History of Israel and God's involvement such as establishing King David and his legacy which led to Jesus Christ his most famous descendant of all.
Prophetic Books of the Old Testament
The Prophets take up a large body of space. They range from the Book of Isaiah and the Book of Jeremiah who are classified as the major prophets to Hosea, Joel, and Jonah who are minor prophets. Prophets were divinely appointed spokesman for God. The Hebrew word for prophet 'nabi' means spokesman. They preached about the corruption of Israel, God's judgement and His future restoration. One vital cornerstone that has bearing for us would be the coming of the Messiah. This is mentioned in Isaiah 53 in the major prophets and last chapters of Zechariah in the minor.
Old Testament History
The Old Testament tells the story of God interacting with his people. It is history. It records stories about real people with real experiences and real emotions, living in a real society. However, it is not exhaustive - it doesn't record all that happened.
In the book How To Read The Bible For All Its Worth, it was suggested that there are 3 levels to Old Testament history
- God's overall plan for his creation
- Israel's role in that plan
- Individual people within that plan
A brief timeline is below
- Genesis 1-11 - Undated - Creation, Fall, Flood, Babel
- Genesis 12-50 - Around 2000 BC - The Patriarchs
- Exodus - Around 1400 BC - From Ancient Egypt to the Promised Land
- Joshua and Judges - Around 1400 BC to 1050 BC - Settling in the Promised Land
- 1 Samuel, 2 Samuel and 1 Chronicles - 1100 BC to 971 BC - Beginning of the Monarchy
- 1 Kings, 2 Kings and 2 Chronicles - 971 BC to 539 BC - The Divided Kingdom and the Exile
- Ezra and Nehemiah - 539 BC to 410 BC - The return from the Exile
Old Testament Themes and Theology
The Old Testament sets the stage for what happens in the New Testament. Its overall theme is about God reaching out his hand of love and mercy to his people. Some of the key themes in it include
Old Testament Geography
An understanding of the geography of the region brings he stories of the Old Testament to life. There are 4 geographical north-south regions of Israel, in order of west to east:
- Flat and fertile plains along the coast
- Valleys and hills
- The Jordan Rift Valley
- Highland regions (now in modern day Jordan)
Old Testament Maps
Abraham's journey from Ur to the promised land
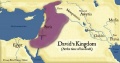
The kingdom of Israel, around the time of King David, showing surrounding empires
Literature from the ancient Near East
Apart from the Old Testament, there is other literature from that time and region. Some of this literature includes creation stories and myths (such as the Enuma Elish), records from royal courts, conventants and laws, and poetry and wisdom literature from other ancient civilizations. These can be useful to help give more context (both in terms of type of literature and also in dating) to the Old Testament.
Quotes
Links
Return to Christianity -> Bible